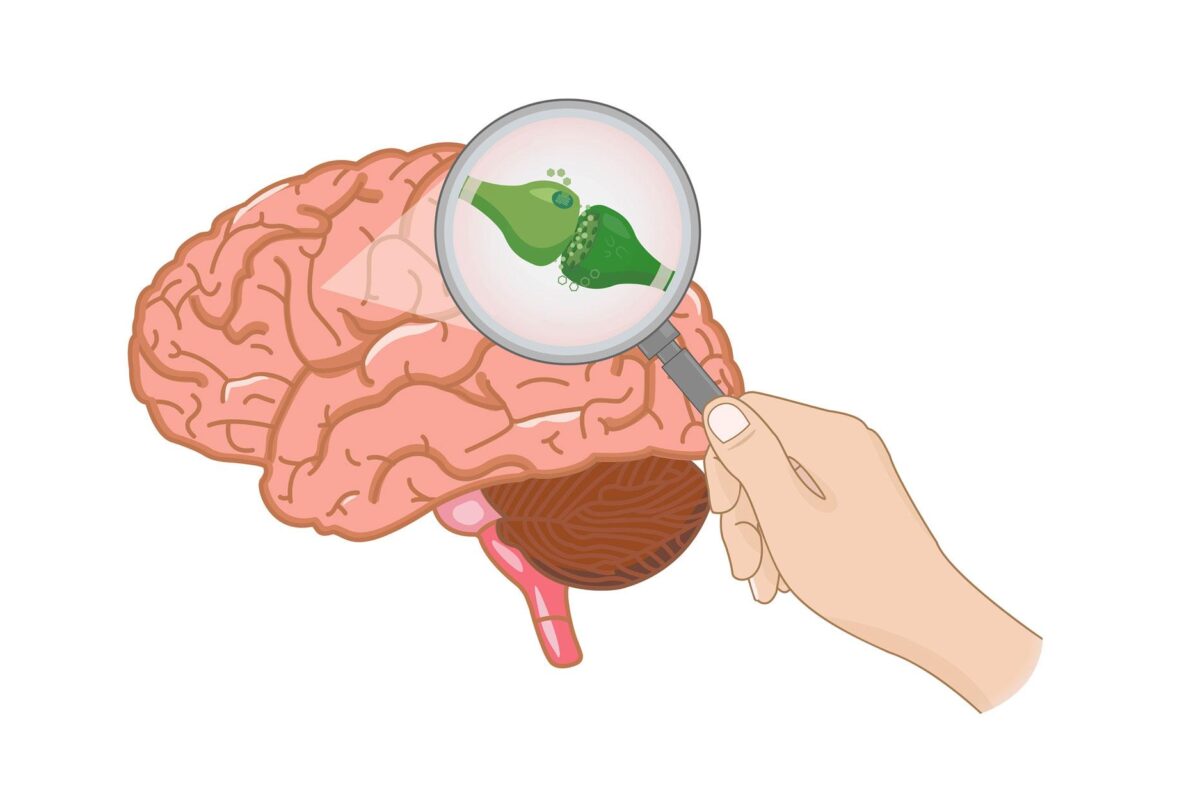
Why is the ECS so important? Because its main duty is to maintain homeostasis in the body. Through the endocannabinoids and the cannabinoid receptors it is able to not only detect and identify disbalances in the body, but deploy its own endocannabinoids to specific receptors, creating a chemical response, and bringing that disbalanced system back into balance.
But what if the body doesn’t make enough?
If the body doesn’t produce enough of its own Endocannabinoids, then ECS can not function properly causing health problems.
This is why supplementing with cannabinoids, such as CBD and THC, can help add to the body’s natural Endocannabinoids and aid the ECS system in bringing the body back into homeostasis. Which is why so many people who have supplemented with CBD and THC report an array of benefits.
Let’s explore the endocannabinoid or ECS system…
Within the body, the ECS system is also known as the “Master regulator” and it’s responsible for the regulation and biochemistry of different bodily processes. Our body naturally produces this ECS as a cannabis-like compound that is then carried by our nerve cells. The three main components within the ECS are:
Endocannabinoid, (AEA) and (2-AG)(EPA and DGLA)
Cannabinoid receptors (CB1) and (CB2)
Enzymes. (FAAH) and (MAGL)
Endocannabinoids include Anandamide (AEA), a neurotransmitter, and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), two essential fatty acids. These endocannabinoids are very chemically similar to the cannabinoids as is CBD and THC, but….. they are naturally created by the body.
(AEA) Anandamide as a neurotransmitter is referred to as the “bliss molecule” for its euphoric role and its similarities in structure to THC. Due to its neurogenesis, AEA also contains anti-anxiety and anti-inflammatory effects, which further positively affects other body functions such as: Motivation, pain, temperature regulation, appetite, and fertility.
(2-AG) 2-arachidonoylglycerol, are two essential fatty acids, known as (EPA) and (DGLA), which are considered the most abundant in the body. (2-AG) and (AEA) have very similar properties and together play an important role in immune system functions, pain management, and appetite. It also regulates and adjusts anxiety, depression, addictive behaviours and the multiplying of certain cancer cells.
Cannabinoid receptors (CB1) and (CB2)
These Endocannabinoids receptors are not only found throughout the body but they serve two major functions. They govern the effects of (AEA) and (2-AG) and also regulate the behavioral effects of cannabis.
(CB1) are primarily found in the brain and spinal cord, Whereas (CB2) are found throughout the peripheral nervous system. Even though both receptors are found throughout the nervous system each have individual areas of focus.
CB1, is responsible for the production of serotonin, dopamine and opioid receptors.
CB2, are found in your immune system, organs and bones.
Enzymes: Endocannabinoid Recycling, these enzymes in the nerve cells break down the endocannabinoids back into their original components to be reused by the next neurotransmitter. The two enzymes found in the ECS are:
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) which breaks down AEA
Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) which breaks down 2-AG
How does CBD work in the brain and body?
Think of CBD as a promiscuous molecule that flirts with many kinds of receptors to get a different reaction from each receptor it interacts with.
The ECS system regulates sleep, anxiety, depression, bone growth, immune system function, digestion, stress, inflammation and a host of other body functions.
Our bodies have a set of receptors that interact with the cannabis compound called Cannabinoids, like CBD. These receptors found throughout the body, comprise the endocannabinoid system (ECS) which is a complex signaling system that ensures our bodies maintain homeostasis.